Few firms that extend credit to customers are immune to credit losses. Credit losses are regarded as operating expenses of the business and are debited to an appropriately titled account such as Uncollectible Accounts Expense. Other account titles frequently used are Loss from Uncollectible Accounts,Loss from Doubtful Accounts or Bad Debts Expense. Normally, the expense is classified as a selling expense on the income statement, although some companies may include it with administrative expenses.
There are two acceptable methods for recognizing losses from uncollectible accounts. One is called the direct write-off method. Under this method, bad accounts are charged to expense in the period when they are discovered to be uncollectible. The other method, which is preferable, is called the allowance method. This procedure not only matches credit losses with related revenue, but also results in an estimated realizable amount for accounts receivable in the balance sheet at the end of the period. The estimate is introduced into the accounts by means of an adjusting entry.
Estimates of credit losses are generally based on past experience, with due consideration given to forecasts of sales activity, economic conditions and planned changes in credit policy. The most commonly used calculations are related either to credit sales for the period or to the amount of accounts receivable at the close of the period.
Estimates Related to Credit Sales Suppose that credit sales for a period amount to $ 20 000 and that past experience indicates a loss of 1. 5%. The adjusting entry to provide for expected losses would be:
Dec. 31 Uncollectible Accounts Expense 300
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts 300
Estimates Related to Accounts Receivable A company’s experience may show that at the end of a period a certain percentage of Accounts Receivable is likely to prove uncollectible. The credit balance in the allowance account should be equal to this amount. Therefore the company may simply derive the adjustment for uncollectibles as the amount needed to create the desired credit balance in the allowance account. Suppose that a particular company estimates uncollectibles as 5% of Accounts Receivable and that the Accounts Receivable balance at the end of an accounting period is $ 5 000. Therefore, the credit balance desired in the allowance account is $ 250. If the allowance account already has a residual credit balance of $ 40,the amount of the adjustment will be $ 210.
Instead of using a fixed percentage of the aggregate customer’s balances, some companies will determine the amount needed in the allowance account after analyzing the age structure of the account balances. In order to do this, they will prepare an aging schedule as follows:
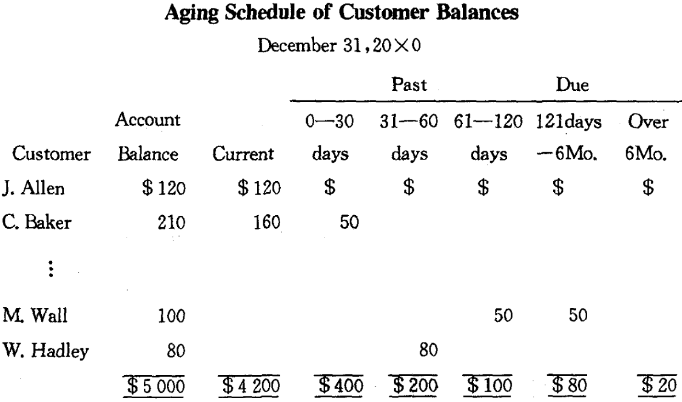
Companies may analyze their bad accounts experience with the aged balances over time, and develop respective percentages of all strata that they think are likely to prove uncollectible. Applying the percentages to the totals in our aging schedule, we can calculate an allowance requirement of $ 156.
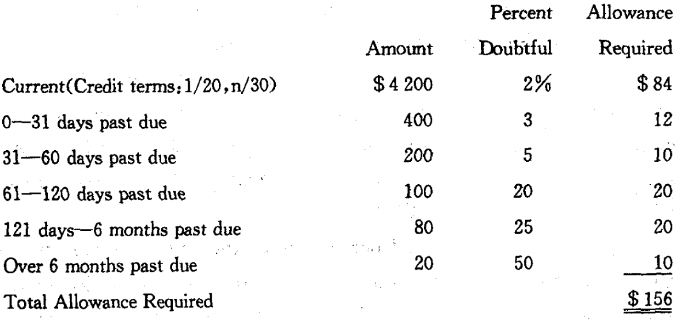
Again,if the allowance account had a residual credit balance of $ 40 the adjustment would be for $ 116.
Dec. 31 Uncollectible Accounts Expense 116
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts 116
When a specific account is determined as uncollectible it would be written off through the allowance account.
Jan. 5 Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts 50
Accounts Receivable-M Wall 50
Note that this entry to write off an account has no effect on net income or on total assets. The expense was reflected, by means of the adjusting entry, in the period when the related revenue was recorded. Furthermore, since the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts is deducted from Accounts Receivable in the balance sheet, the net realizable amount of Accounts Receivable is not changed by the write-off.
New Words, Phrases and Special Terms
Notes to the Text
1. Under this method, bad accounts are charged to expense in the period when they are discovered to be uncollectible.
用关系副词when引导的定语从句,修饰the period。
2. Estimates of credit losses are generally based on past experience, with due consideration given to forecasts of sales activity,economic conditions and planned changes in credit policy.
with引导的介词短语中,due consideration given to…是复合宾语(过去分词短语given to…作补语)。with后加复合宾语,常用作状语说明方式,有时则是说明附带的情况(如句中)。
3. Companies may analyze their bad accounts experience with the aged balances over time and develop respective percentages of all strata that they think are likely to prove uncollectible.
(1)全句中,用and连接的并列谓语的后一部分develop…percentages …中,包含一个修饰percentages (of all strata)的定语从句that…uncollectible,关系代词that在从句中作主语。
(2)这一定语从句中还包含一个插入语they think。
READING MATERIAL
TRADE RECEIVABLES AND PAYABLES
The terms trade receivables (应收账款)and trade payables (应付账款)usually refer to receivables and payables arising in regular course of the company’s transactions with customers and suppliers. Payments normally are to be made within 30 to 60 days. If an advance(预付款)is made to an employee or officer of the company, it should not be included here, nor should advances to affiliated companies (关联公司),such as subsidiaries (子公司),be included. Such receivables should be recorded in separate accounts. In many instances such receivables are not current, and as a result, these items are often seen in the balance sheet under a noncurrent heading as Other Assets. Advances to subsidiary companies are frequently semi-permanent, and they are found in the balance sheet under the Investments caption.
Likewise, trade accounts payable consist only of open(尚未偿付的) accounts owing to the purchase of merchandise or materials or to the acquisition of services from outsiders. Amounts that a firm owes for salaries and wages and for various types of taxes,sundry accruals,and so on are recorded in separate current liability accounts.
The principal reason for separating trade accounts from other receivables and payables is to facilitate analysis by both the management and outsiders.
