Depreciation can be caused by wear from use, natural deterioration through interaction of the elements and technical obsolescence. Many accountants contend that long-term assets are actually “bundles of services or utility” and that their rate of depreciation should be related in some way to the pattern in which these services are used to generate revenues. For many assets, particularly assets affected by rapid technological change,one can argue that the utility is more rapidly consumed in the earlier periods of useful life than in the later periods.
The most commonly used depreciation methods are:the straight-line method, the units-of-production method, the sum-of-the-year’s-digits (SYD) method and the double-declining-balance (DDB) method. The SYD method and the DDB method "accelerate” depreciation expense so that the amounts recognized in the earlier periods of an asset's useful life are greater than those recognized in the later periods.
Straight-line Method Straight-line depreciation is probably the simplest to compute. An equal amount of depreciation expense is allocated to each full period of the asset’s useful life. Using straight-line depreciation,
![]()
which in our example (cf. the diagram in the previous lesson) is
![]()
This method of uniform allocation is best suited to assets whose periodic usage is relatively uniform and whose obsolescence factor is low. Examples include pipelines, storage tanks,fencing and surface paving.
Units-of-Production Method The units-of-production method allocates depreciation in proportion to the degree the asset is used for production. The depreciation per unit of production is computed by dividing the total expected depreciation by the estimated units- of-production capacity (in miles driven,tons hauled, number of cuttings, drillings or stampings of parts, etc. ) that has been projected for the asset. Thus,
![]()
Assume that our example is a drilling tool that will drill an estimated 45 000 parts during its useful life. The depreciation per unit of production is
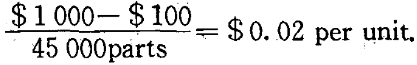
If 8 000 units were produced during the first year,then 8 000×$0.02=$ 160 would be this year’s depreciation expense. If 12 000 parts were drilled the next year, that year’s depreciation expense would be 12 000×$ 0. 02= $ 240.
The units-of-production approach is particularly appropriate when wear is the major cause of depreciation and the amount of use varies from period to period.
Sum-of-the-Year’s-Digits Method By the SYD method, the yearly depreciation is calculated by multiplying the total depreciable amount for the life of the asset by a fraction whose numerator is the remaining useful life and whose denominator is the SYD. Thus,
![]()
The calculations for our example are shown below:
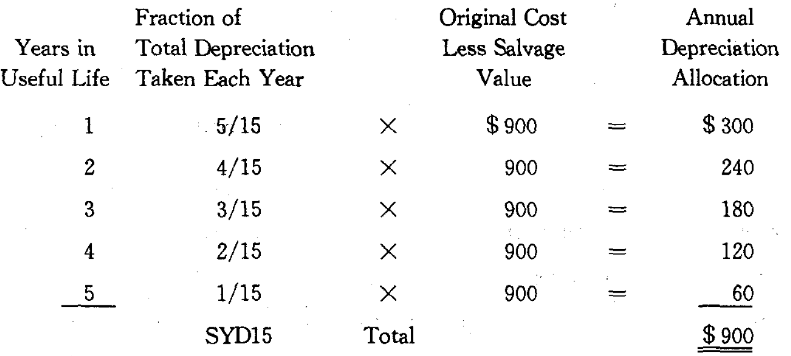
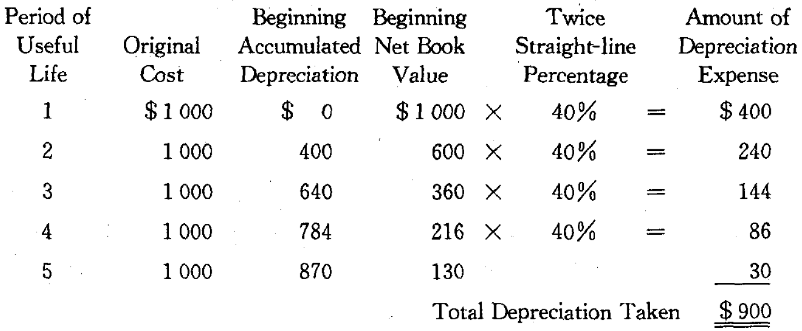
Double-Declining Balance Method Another accelerated depreciation method is the DDB method, which derives its name from the fact that a constant percentage factor, twice the straight-line rate, is determined and applied each year to the declining balance of the asset’s book value. The straight-line rate is simply the number of years in the asset’s useful life divided into 100%. In our example, this would be 100%/5 = 20%. Double the straight-line rate is then 40%. In equation form,
![]()
Observe that in the fifth year depreciation expense is only $ 30,the amount needed to reduce the asset’s book value to the estimated salvage value of $ 100. Assets are not to be depreciated below their salvage values. If no salvage value has been estimated, the double-declining-balance technique automatically provides for some salvage value(here $ 78).
As we have mentioned above,the accelerated depreciation method is most appropriate for those situations in which the asset is judged to render greater utility during its earlier life and less in its later life. An accelerated pattern of depreciation is suitable for assets with either a high technological obsolescence factor in the early life phase or a high maintenance factor in the late life phase. In addition, there are certain financial advantages that can be derived from using one of the accelerated depreciation methods as opposed to the straight-line method for income tax reporting purposes. In a sense, accelerated depreciation provides an interest free loan to the taxpayer, because the accelerated methods allow the taxpayer to pay less tax in the earlier phase of the asset’s life and more in the later phase.
Accounting for depletion of natural resources is comparable to units-of-production depreciation for constructed fixed assets. Intangible assets are amortized over the shorter of the economic life or the legal life (if any) , with a maximum amortization period of 40 years as specified in Opinion No. 17 by the Accounting Principles Board of the AICPA.
New Words, Phrases and Special Terms

Notes to the Text
1. Many accountants contend that long-term assets are actually "bundles of services or utility” that their rate of depreciation should be related in some way to the pattern in which these services are used to generate revenues.
(1)全句包含用连词and连接的两个并列的宾语从句,分别用连词that 引导。
(2)在第二个宾语从句中还包含一个修饰the pattern的定语从句,用关系代词which引导,which在定语从句中作介词in的宾语。
2. For many assets one can argue that the utility is more rapidly consumed in the earlier periods of useful life than in the later periods.
(1)全句包含一个用连词that引导的宾语从句。
(2)这一宾语从句属比较结构,处于对比地位的是两个介词短语in the earlier periods of useful life 和in the later periods (of useful life)。
3. If 8 000 units were produced during the first year,then 8 000 ×$ 0.02 =$160 would be this year’s depreciation expense.
(1)全句包含一个用连词if引导的表示虚拟条件的状语从句。
(2)条件状语从句中的谓语动词were和主句中的谓语动词would be 都属虚拟语气。
4. The units-of-production approach is particularly appropriate when wear is the major cause of depreciation and the amount of use varies from period to period.
句中用when引导的时间状语从句是由两个并列的分句构成的(用连词and连接)。
5. Another accelerated depreciation method is the DDB method, which derives its name from the fact that a constant percentage factor,twice the straight-line rate,is determined and applied each year to the declining balance of the asset’s book value.
(1)全句包含一个用关系代词which引导的非限制性定语从句,用以修饰the DDB method.
(2)定语从句中,介词from的宾语是the fact及其同位语从句(用连词that引导)。在这一同位语从句中,用连词and连接了两个并列的谓语:is determined and (is) applied…to…。
6. As we have mentioned above, the accelerated depreciation method is most appropriate for those situations in which the asset is judged to render greater utility during its earlier life and less in its later life.
(1)全句包含一个用连词as引导的方式状语从句。
(2)主句中又包含一个修饰those situations的定语从句(用关系代词which引导,which在从句中作介词in的宾语)。
READING MATERIAL
CONTROL OF FIXED ASSETS
Firms with a large number of fixed assets normally maintain some formal records and follow systematic inventory procedures so that specific persons can be held accountable for the asset’s use and protection. Many firms assign a specific serial number (顺序编号) to identify each significant asset. This is usually done by small decals, stampings, or etchings that are not easily removed or altered.
Coupled with the identification procedures will be a formal record of the assets called a plant ledger or an equipment ledger. This record is often a subsidiary ledger to the various fixed asset accounts. Certain basic data are usually provided. The following list is representative:Description
Manufacturer's identification(制造厂商鉴定书)or model number(型号)
Firm’s assigned serial number and accounting classification
Date purchased
Assigned physical location
Person accountable
Original Cost
Major modifications and repairs
Depreciation method and data
Disposition Data (清理数据)(date, price, remarks)
This record requires that any purchase, transfer or disposition of property be formally noted. Also,a company should periodically verify its equipment ledger by a physical count of the items involved.
